VegOil: Why Australia Chooses Malaysia, Not Indonesia?
Talk to our team about AgFlow's offering →
Reading time: 2 minutes
Australia, a land known for its diverse agricultural produce, is a key player in the global trade of vegetable oils. In this article, we delve into the intricate web of factors influencing Australia’s vegetable oils trade and imports in the first eight months of 2023, shedding light on the key drivers, challenges, and trade-offs shaping this dynamic industry.
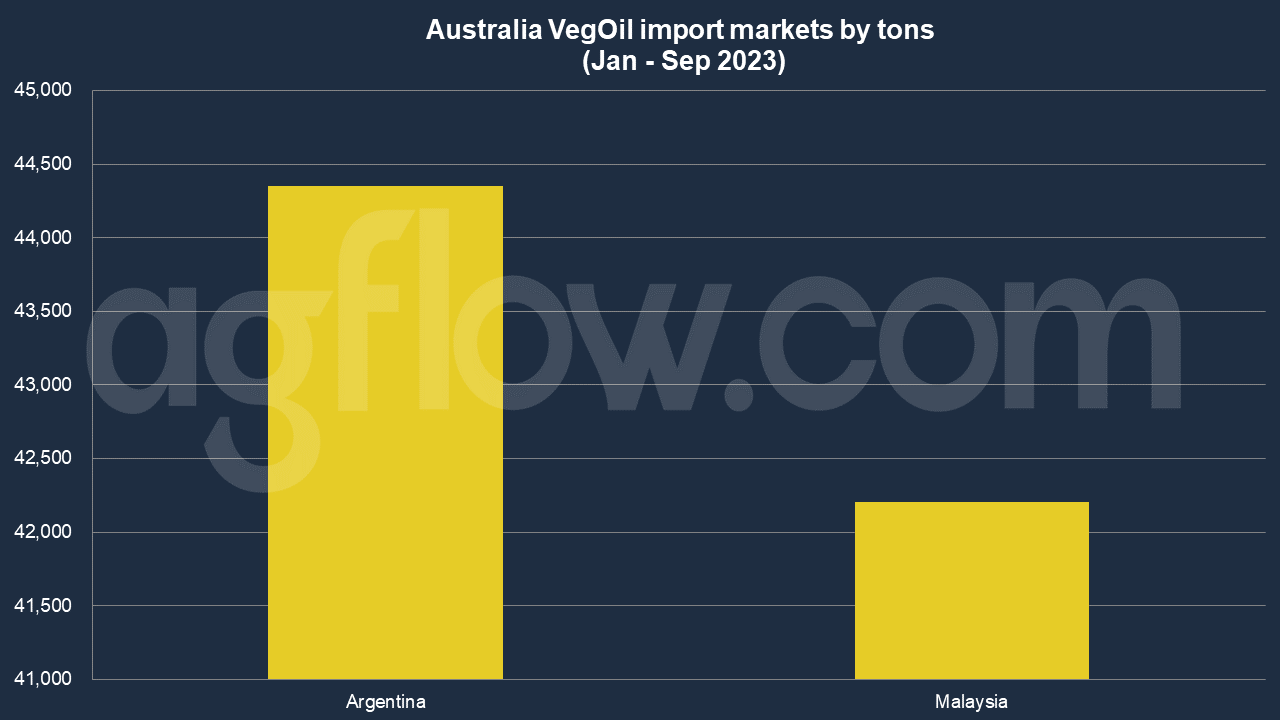
According to AgFlow data, Australia imported 44,350 tons of Vegetable Oil from Argentina in Jan – Sep 2023, followed by Malaysia (42,205 tons). Malaysia shipped mostly RBD Palm Oil and Olein. Total imports hit 90,557 tons. Average volume of shipments was 2,829 tons.
In 2021, Australia imported Palm Oil worth $79.9 million, becoming the 69th largest importer of Palm Oil in the world. At the same year, Palm Oil was the 385th most imported product in Australia. Australia imports Palm Oil primarily from: Malaysia ($77.4 million), Singapore ($1.4 million), New Zealand ($673k), Colombia ($120k), and Japan ($109k).
Supply and Demand Dynamics
The foundation of Australia’s vegetable oils trade rests on the interplay between supply and demand. The country’s production of vegetable oils, primarily canola and soybean, plays a pivotal role in meeting domestic demand and fulfilling export commitments. Factors such as weather patterns, crop yields, and global market fluctuations significantly impact this equilibrium.
International Market Trends
The global vegetable oil market is a complex arena influenced by factors ranging from geopolitical events to health trends. In 2023, the increased demand for healthier cooking oils and the push for sustainable sourcing are driving shifts in consumer preferences and influencing Australia’s trade strategy. How does Australia adapt to these trends without compromising on quality or sustainability?
Trade Agreements and Tariffs
Trade agreements, or the lack thereof, profoundly impact Australia’s vegetable oil trade. The country’s negotiations with key trading partners, such as the ASEAN nations and China, can determine the success or failure of export ventures. Tariffs and non-tariff barriers, including strict quality and safety standards, pose both opportunities and challenges.
Sustainable Practices
Sustainability is a critical concern in the vegetable oil industry, with consumers and governments increasingly pushing for eco-friendly practices. Australia’s ability to adhere to sustainable sourcing and production standards enhances market access and fosters long-term viability for the industry. However, this transition comes with its own set of challenges and costs.
Domestic Consumption vs. Export
Balancing domestic consumption with export commitments is a perpetual challenge for Australia’s vegetable oil industry. How does the nation prioritize the needs of its growing population while maintaining its position as a global vegetable oil exporter? This dichotomy underscores the importance of efficient supply chain management.
Currency Exchange Rates
Currency exchange rates can either boost or hinder Australia’s vegetable oil exports. Fluctuations in the Australian dollar can impact the competitiveness of Australian products in international markets. How do traders and policymakers navigate this volatile terrain to ensure stability in the trade balance?
Weather and Climate Change
Australia’s susceptibility to extreme weather events, exacerbated by climate change, can disrupt the vegetable oil supply chain. The unpredictability of weather patterns poses a constant challenge for farmers and exporters alike, emphasizing the need for adaptive strategies and risk mitigation.
Regulatory Compliance
Stringent regulatory compliance in both domestic and international markets is a significant aspect of vegetable oil trade. Meeting food safety and quality standards is imperative to maintain Australia’s reputation as a reliable source of vegetable oils.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Australia’s vegetable oils trade and imports in 2023 are influenced by many factors, from supply and demand dynamics to global market trends, trade agreements, and sustainability concerns. Achieving a balance between these factors is the key to ensuring the industry’s resilience and continued growth.
As we move forward, it is crucial for Australia to remain adaptable, make informed decisions, and invest in sustainable practices to secure its position in the competitive global vegetable oils market. By addressing the challenges and trade-offs head-on, Australia can continue to be a prominent player in the agricultural commodity industry, meeting the needs of both its domestic and international stakeholders.
Try AgFlow Free
Access Free On Updates for Corn, Wheat, Soybean,
Barley, and Sunflower Oil.
No Credit Card Required & Unlimited Access In Time

